Virus Meaning In Biology
Viruses infect cells of microorganisms plants and animals and whilst they carry out no metabolism themselves they are able to control the metabolism of the infected cell. In biology viruses are microscopic entities that are able to replicate inside the cell of its host.
12 1 Viruses Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
The definition of viruses differs among scientists because these entities can neither be classified as living organisms nor non living entities.

Virus meaning in biology. A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. In infection the virus interacts with the host cell surface and penetrates the cell. Virus definition a virus is a chain of nucleic acids dna or rna which lives in a host cell uses parts of the cellular machinery to reproduce and releases t a virus is a chain of nucleic acids dna or rna which lives in a host cell uses parts of the cellular machinery to reproduce and releases the replicated nucleic acid chains to infect more cells.
Viruses are infectious agents that replicate inside the body of a host. Virus nucleic acid is replicated and virus components are synthesized inside the cell. Viruses infect all types of life forms from animals and plants to microorganisms including bacteria and archaea.
 Viruses And Bacteria Complete Unit Plan 14 Products Included Science Student Biology College Science Biology
Viruses And Bacteria Complete Unit Plan 14 Products Included Science Student Biology College Science Biology
 Steps Of Virus Infections Text Version Biology For Majors Ii
Steps Of Virus Infections Text Version Biology For Majors Ii
 Bacteriophage Online Textbook Ap Biology Immunology
Bacteriophage Online Textbook Ap Biology Immunology
 Pin By Hadjih On Biologie Prokaryotes Genetic Variation Biology
Pin By Hadjih On Biologie Prokaryotes Genetic Variation Biology
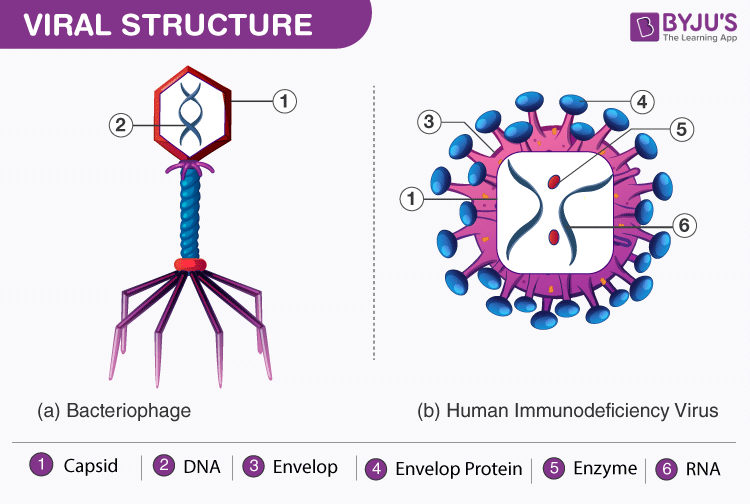 What Are Viruses Discover The Classification And Properties Of Viruses
What Are Viruses Discover The Classification And Properties Of Viruses
 Download Six Types Of Viruses On White Background For Free Biology Art Biology Projects Biology
Download Six Types Of Viruses On White Background For Free Biology Art Biology Projects Biology
 Virus Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help
Virus Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help




Post a Comment for "Virus Meaning In Biology"