Virus Host Cell Interaction
One or more virions infect a host cell which is then converted into a factory for the synthesis of new viruses. Types of virus host interactions.
 Virus Replication British Society For Immunology
Virus Replication British Society For Immunology
Virus host interactions are exemplifying by lytic virus multiplication.

Virus host cell interaction. Many viral infections are asymptomatic or silent whereby the virus replicates within the host but does not produce symptoms of a disease. Virus attachment protein vap attaches to the receptor of the host cell. However this is not the only possible type of virus host interaction.
The non specific host defenses function early in the encounter with virus to prevent or limit infection while the specific host defenses function after infection in recovery immunity to subsequent challenges. The defenses mounted by the host may act directly on the virus or indirectly on virus replication by altering or killing the infected cell. Lack of membrane receptors viruses gain entry into host cells by first binding to specific receptors on cells dr t v rao md 11 12.
Receptor on the host cell enable virus to gain entry into the host cell. There is a great diversity in viral infections and viral diseases. Virus host interactions justin stebbing brian gazzard the co existence of viruses with their hosts can be viewed as a molecular arms race between the virus and host elimination mechanisms.
The viral vmia protein green is present in mitochondria in both but the actin cytoskeleton red is disrupted only in the viperin expressing cells. The cell infection processes and host ranges of canine parvovirus cpv and feline panleukopenia virus fpv are controlled by their capsid interactions with the transferrin receptors tfr on. This term is most commonly used to refer to disease causing microorganisms although they may not cause illness in all hosts.
Continuous interactions between hosts and pathogens during their co evolution have shaped the immune system and in. Receptors on host cells the cells surface molecule contains glycoprotein and glycolipid. In some instances the mucus simply acts as a barrier but in other cases the mucus can prevent infection by competing with virus receptors on cells.
Mucus the mucus covering an epithelium acts as a barrier to prevent infection of host cells. Fusion direct penetration endocytosis. Because of this the definition has been expanded to how known pathogens survive within their host whether they cause disease or not.
The three different routes are. Virus can enter the host cells through three different routes. On the molecular and cellular level microbes can infect the host.
The host pathogen interaction is defined as how microbes or viruses sustain themselves within host organisms on a molecular cellular organismal or population level. Virions accumulate in the cell which eventually disintegrates and scatters its contents. In wild type left and viperin knockdown right fibroblasts that are infected by human cytomegalovirus viperin is induced only in the wild type cells.
The interaction with the host cell will vary between viruses but will generally follow one of these five routes.
Virus Infections And Hosts Biology Ii
 Dna Viruses In Eukaryotes Boundless Microbiology
Dna Viruses In Eukaryotes Boundless Microbiology
 The Viral Life Cycle Microbiology
The Viral Life Cycle Microbiology
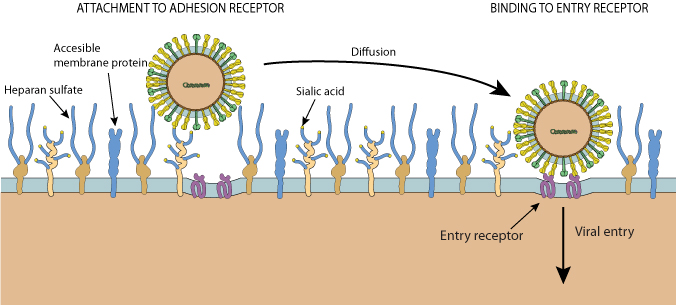 Viral Attachment To Host Cell Viralzone Page
Viral Attachment To Host Cell Viralzone Page
 Biology Of The Influenza Virus Infectious Disease Superbugs Science Society
Biology Of The Influenza Virus Infectious Disease Superbugs Science Society
 Interactions Between Retroviruses And The Host Cell Genome Molecular Therapy Methods Clinical Development
Interactions Between Retroviruses And The Host Cell Genome Molecular Therapy Methods Clinical Development
 Steps Of Virus Infections Biology For Majors Ii
Steps Of Virus Infections Biology For Majors Ii
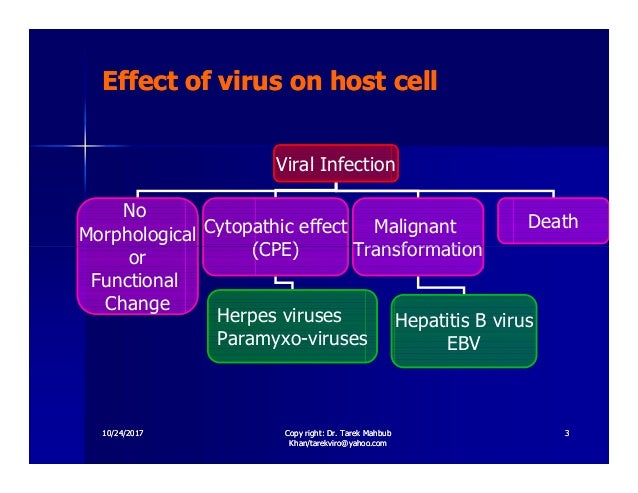 Virus Cell And Virus Host Interaction Virology 7
Virus Cell And Virus Host Interaction Virology 7
 Virus Genome An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Virus Genome An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Virus Release An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Virus Release An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Post a Comment for "Virus Host Cell Interaction"