At least three major modes of entry. The virus does so by either attaching to a receptor on the cell s surface or by simple mechanical force.
The Viral Life Cycle Microbiology
There are no symptoms until the virus enters the lytic cycle.
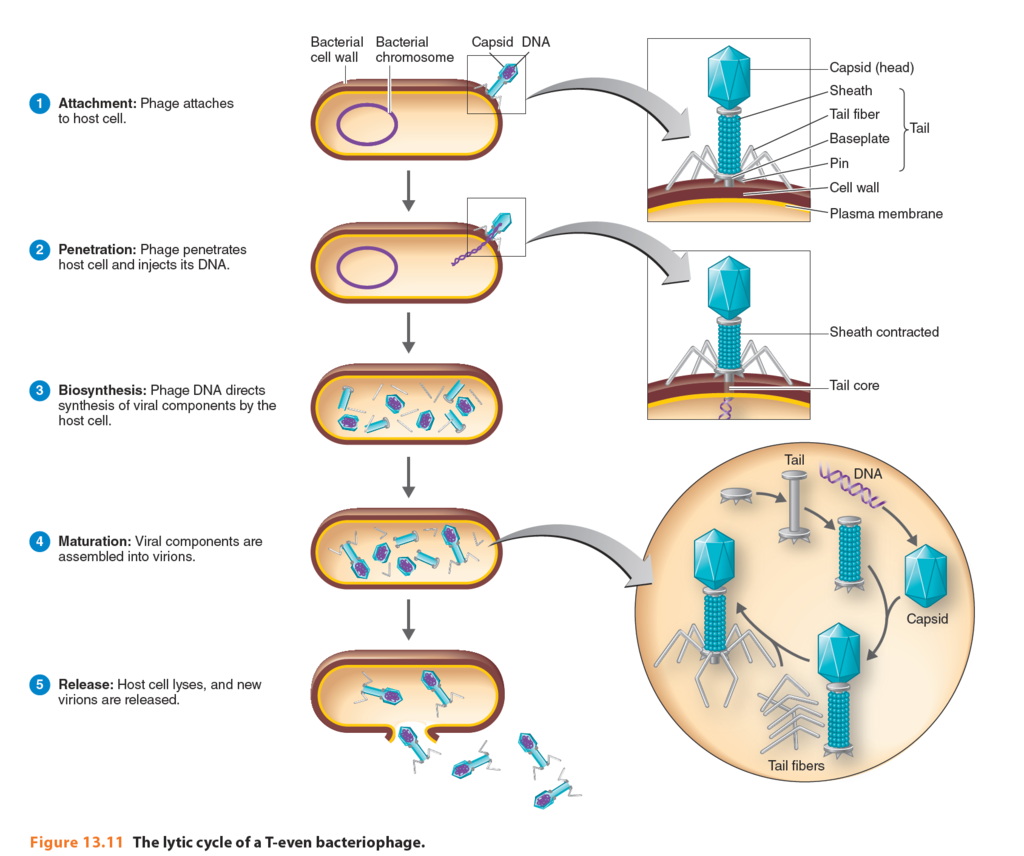
Virus nucleic acid is injected into host cell. Some viruses inject their nucleic acid whereas others must also ensure that a virus associated rna or dna polymerase enters the cell. A virus injects its dna or rna into a cell resulting in the production of viral proteins by the host cell. Basically the virus injects genetic information which the host cell is tricked into using.
In some viruses this genetic material. The component of a virus nucleic acid is injected into an infected cell. Replication viral dna inactivates host cell s dna uses host s raw materials ribosomes to make viral dna capsids tails etc.
The dna or rna of the virus enters the cell and integrates with the dna of the host cell and a provirus is formed. In the case of t4 the host rna polymerase binds to the viral dna and begins transcribing early genes immediately after the dna is injected into the cell. Once inserted into host cells this genetic material is read by the cell s own protein making machinery and used to manufacture antigens which then trigger an immune response.
Eddibear3a and 125 more users found this answer helpful. The virus then releases its genetic material either single or double stranded rna or dna into the cell. Assembly new viral parts are combined to make new phages.
The virus enters the lytic cycle and symptoms appear. The binding is due to electrostatic interactions and is influenced by ph and the presence of ions. This is a relatively new technology so although dna and rna vaccines are being developed against various diseases including hiv zika virus and covid 19 so far none of them have yet been approved for human use.
The provirus replicates with the host cell. It begins with the attachment of the virus to a host cell. The nucleic acid of bacteriophages enters the host cell naked leaving the capsid outside the cell.
Plant and animal viruses can enter through endocytosis in which the cell membrane surrounds and engulfs the entire virus. Some enveloped viruses enter the cell when the viral envelope fuses directly with the cell membrane. All viruses contain a nucleic acid which also carries its deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid.
Injection nucleic acid dna of virus injected into host cell. Via the formation of a pore in the plasma membrane through which the rna is then injected into the host cell cytoplasm or via virus uptake by receptor mediated endocytosis. Some naked viruses undergo a major change in capsid structure on adsorption to plasma membrane so that their nucleic acids are released into the cytoplasm.
The correct answer to the question above is nucleic acid. Adsorption phage attaches to cell membrane of host. The virus often employs strategies for control of gene expression to insure that particular viral products are made at specific times in the virus replication.
To infect a host cell the virus must first inject its own nucleic acid into the cell through the plasma membrane and if present the cell wall. Following attachment to the host cell membrane entry of the viral nucleic acid was thought to occur one of two ways.
The Lytic Cycle Figure 13 11 Diagram Quizlet
Virus Infections And Hosts Biology Ii
Types Of Microorganisms Microbiology Health And Disease
Virus Infections And Hosts Boundless Biology
Virus Infections And Hosts Biology For Majors Ii
Pore Mediated Penetration Of Viral Genome Into Host Cell Viralzone Page
Solved Match The Letter In The Diagram Right With The B Chegg Com
Solved 8 A B Match The Letter In The Diagram Right Wit Chegg Com
Viruses Virus Latin Meaning Poisonous Slime Of Plant Or Animal Origin Viruses Are Non Living 1 Acellular Lack Cell Membrane And Organelles 2 No Ppt Download
Major Parts Of A Virus Bacteriophage Ppt Video Online Download
Biology 102 Viruses Ppt Download

0 comments:
Post a Comment